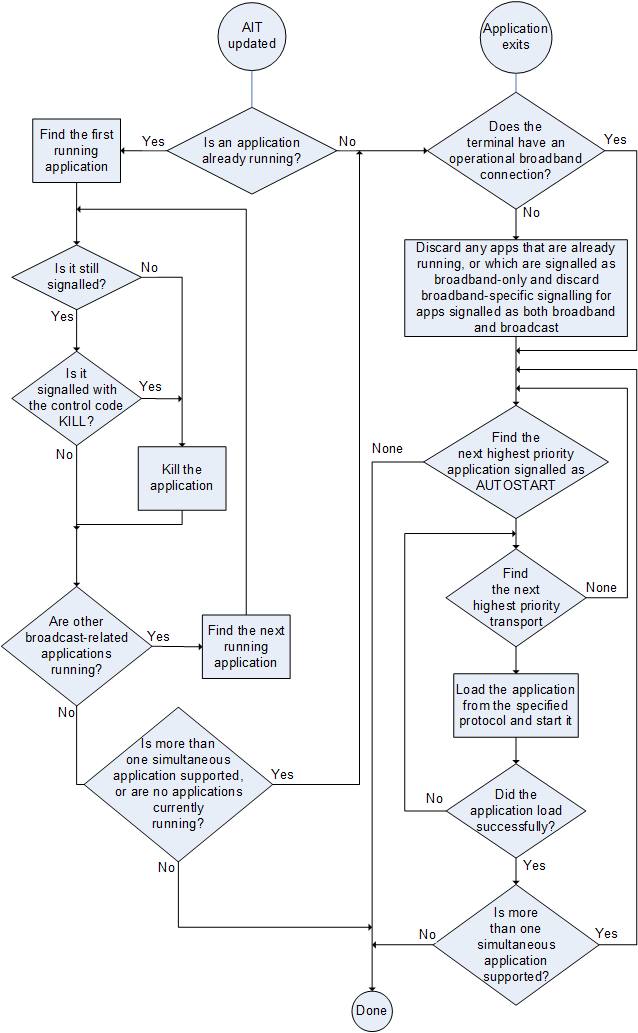
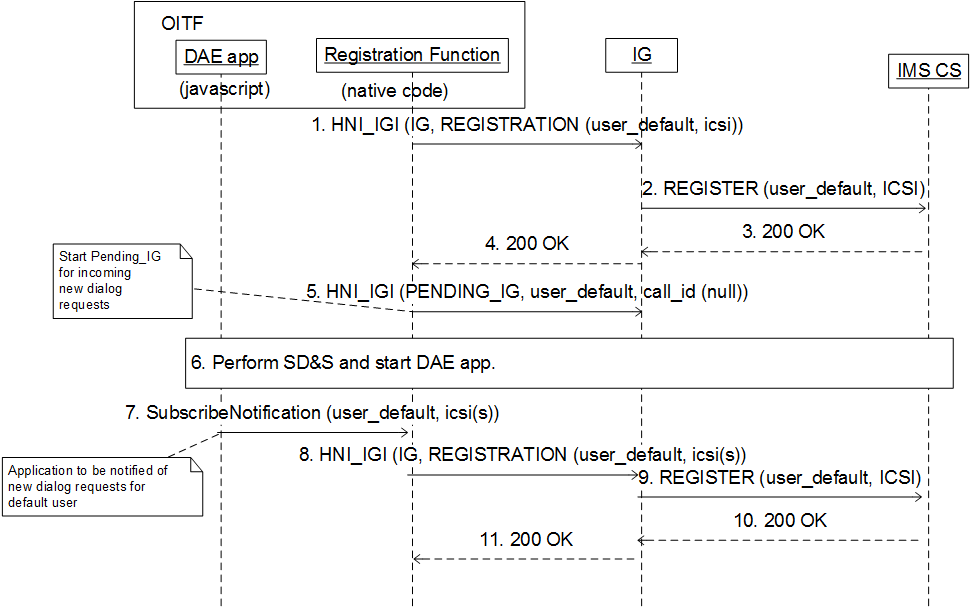
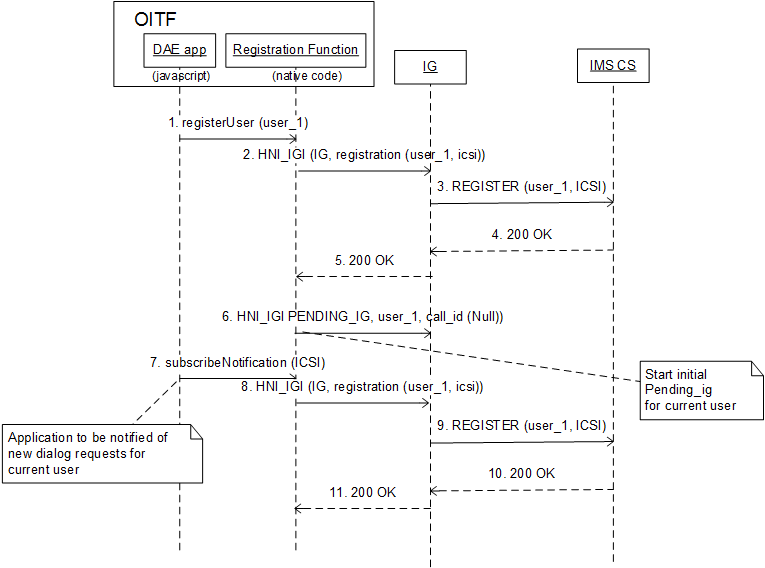
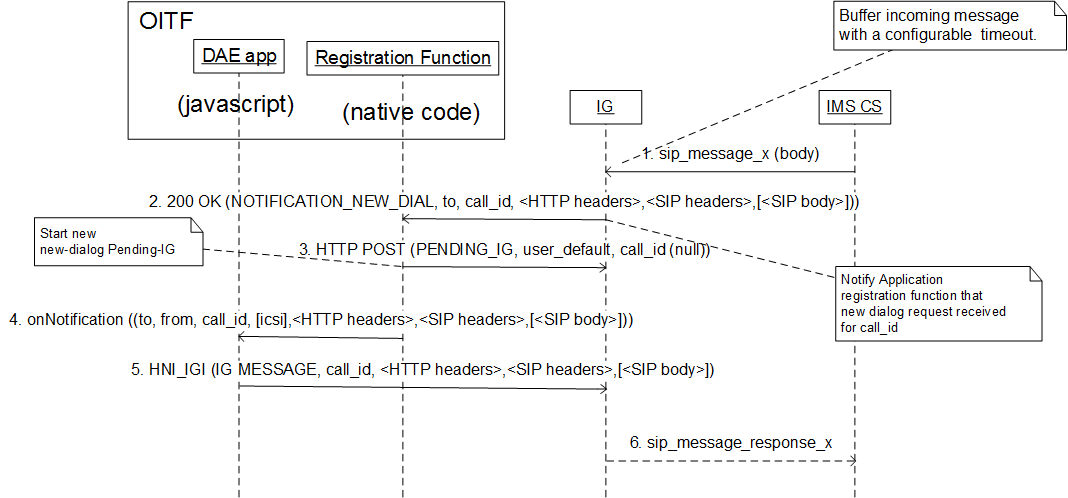
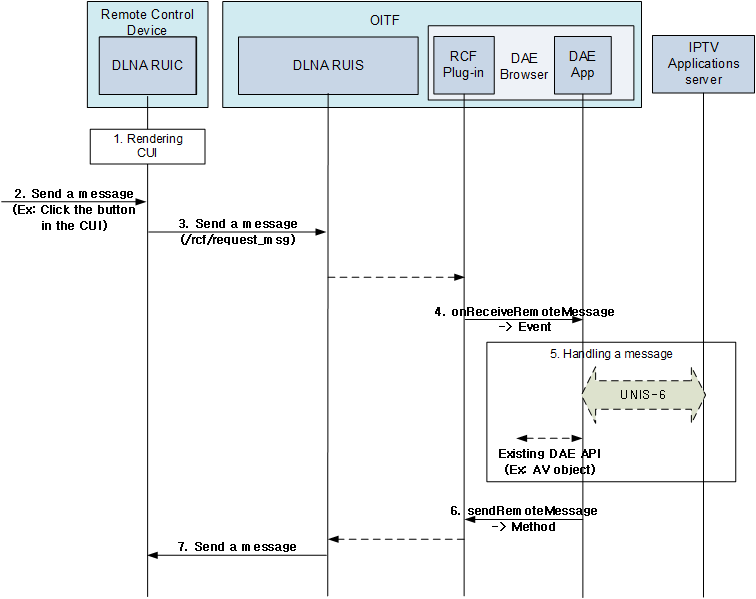
D.2 List of interfaces
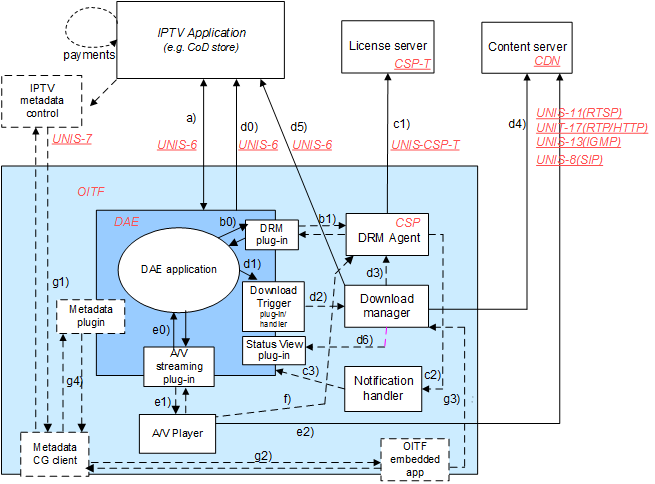
Interface a: browse, select and purchase content from CoD store
This interface is used to interact with the CoD store for operations
such as user registration, browsing the content offered by the CoD
store, and purchase a license. This is a standard CE-HTML/HTTP
interface.
Interface b*: In-session interaction from web page with underlying DRM agent
Interface b0 (and the related interface b1) is the
application/oipfDrmAgent JavaScript embedded object interface as defined
in section 7.3.
This interface will allow messages to be exchanged between pages from
the CoD store and the underlying DRM agent, whilst the user is having a
user interface session with the CoD store. Examples of these messages
are Marlin Action tokens. This is useful to enable scenarios, such as
subscription license acquisition, registration, domain management, etc.
The interface basically consists of one method: sendDRMMessage(String
msgType, String msg), which is very generic in the sense that any kind
of message can be exchanged. The exact payload and types of messages
that could be exchanged is defined in the [OIPF_CSP2]. An example of such message could be:
pluginElement = document.getElementByID("drmplugin");
pluginElement.sendDRMMessage("application/vnd.marlin.drm.actiontoken+xml",
"<marlin>...</marlin>",
"urn:dvb:casystemid:19188");
...
<object id="drmplugin" type="application/oipfDrmAgent"/>
Note that this API is designed to be asynchronous in nature, because
certain interactions may take a indeterminate amount of time. Therefore,
it is not wise to make the method synchronous, since that could block
the JavaScript engine. To this end we have defined an event handler:
onDRMMessageResult, to register a callback function that will be called
when the DRM agent completed handling of the message. For example:
function callbackF(String msgID, String resultMsg, Integer resultCode) {
...
}
document.getElementByID("drmplugin").onDRMMessageResult = callbackF;
An equivalent DOM2 event is also generated.
Content authors should be
aware of the asynchronous nature of the API. Only after having received
the callback message, the web page can assume that the DRM agent has
handled the DRM message. The service author may need to define some
visual cues to the user if he would like the user to wait for certain
actions to finish.
Interface c*: Autonomous out-of-session interaction between DRM agent and CoD store
Interface c1 is the collection of interfaces between the DRM agent, the CoD store, the license server, etc. as defined in the [OIPF_CSP2].
The interaction is typically done outside the scope of the browser, and
also without the user being involved. In the few cases where the user
would be involved, the device will typically have its own “local” user
interface to handle the interaction with the user. In some of these the
DRM agent would need to open a web page to the originating CoD store,
so that the user could resolve the issue directly with the store (e.g.
using the rightsURL extracted from the MPEG2_TS). Since the user could
be doing other things at that moment, it may not be appropriate to
popup/replace the current browser session without the user consent.
Therefore, the DRM agent could issue a notification event that will get
listed along similar lines to a third-party notification event. The user
would be notified that his attention is required with respect to the
DRM agent, and can then decide to take action and launch the browser.
In the figure above, these UI interactions are identified by
interface c2 and c3. These interfaces however are typically local inside
the OITF, and are not specified in more detail.
Interface d*: Downloading content
These interfaces are used for downloading content. In order to
trigger the download, a special content-access descriptor (the content
access download descriptor) with an easily identifiable MIME type “application/vnd.oipf.ContentAccessDownload+xml”
is used. This descriptor contains all the relevant data related to
fetch the content. This content-access descriptor is typically provided
by the CoD store. A browser application can fetch this descriptor in
various different ways, e.g. by following a link or through an
XMLHttpRequest. This is identified by interface d0. The content access
download descriptor and MIME type are defined in Annex E.
It contains elements, such as <ContentURL> which indicates where
the content item can be fetched, and <MetadataURL> to indicate
where additional metadata, such as genre, subtitles, artwork, etc. can
be retrieved from.
Interface d1) (and related interface d2 are used to trigger/register
the download with the download manager. This is done by handing over the
content access download descriptor to the download manager by calling
method registerDownload() on the application/oipfDownloadTrigger
embedded object after retrieving the content-access descriptor e.g.
through XMLHttpRequest. Once the download is registered, the download
manager will take care that the content is downloaded. Since this may be
a lengthy task, the download manager is an independent process from the
browser, that will perform its duty in the background even if the
browser is closed. By making the download manager an independent process
of the browser, the user can in the meantime do other things.
Interface d3 is a local interface that is used to pass optional DRM
messages carried in the content-access descriptor from the Download
manager to the DRM agent. These messages are included as part of one or
more <DRMControlInformation> element inside the content access download descriptor (as defined by Annex E).
These may include messages (such as a Marlin preview license) in cases
where license information and the content to be downloaded can be
packaged together.
Interface d4 is the actual interface for downloading the content. The
protocols that can be used for downloading content are defined in the
Open ITPV Forum Protocols specification document. The default protocol
is HTTP, with support for HTTP Range requests. The HTTP Range requests
are used in order for downloads to be able to resume after e.g. network
failure or device power-down, because as mentioned above, the download
manager is an autonomous component that must continue downloading the
requested content items as a background process, even after a device
power-down or network failure, until it succeeds or the user has given
permission to terminate the download.
Interface d5 defines an interface to enable error recovery for the
download mechanism. It could be used to recover from errors or other
situations that lead to the corruption or deletion of the
content/licenses or a current download to fail. An example usage is as
follows: to be able to refetch the content, and its licenses from the
CoD store the OITF may synchronize with the CoD store by issuing a
secure HTTP GET request to the URL of element <OriginSite> concatenated with “/synchronize”
as defined by the content-access descriptor, after which the IPTV
application offering the content-download replies with an XML document
describing the list of zero or more content IDs that had previously been
downloaded by the given user (i.e. it is assumed that the IPTV
application offering the content download still remembers which content a
user has bought and downloaded before), using for example the following
format:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xs:element name="synchronizelist" type="SynchronizeType"/>
<xs:complexType name="SynchronizeType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="content" type="ContentType"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
<xs:complexType name="ContentType">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="content_ID" type="xs:string" minOccurs="0"
maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:schema>
Example:
<synchronizelist>
<content>
<content_ID>item 1</content_ID>
<content_ID>item 2</content_ID>
...
</content>
</synchronizelist>
NOTE: To authenticate the user, cookies or single sign on may be used.
The OITF may use this
information to decide which content and which licenses to refetch.
Refetching the content is done by issuing a secure HTTP GET request to
the following URL:
<OriginSite> + "/synchronize" + "?" + a <content_ID> value
after which the application offering the content download replies
with the appropriate information to retrigger the download by providing
the appropriate content access download descriptor in order to trigger
the download manager and DRM agent to redownload the content and related
licenses.
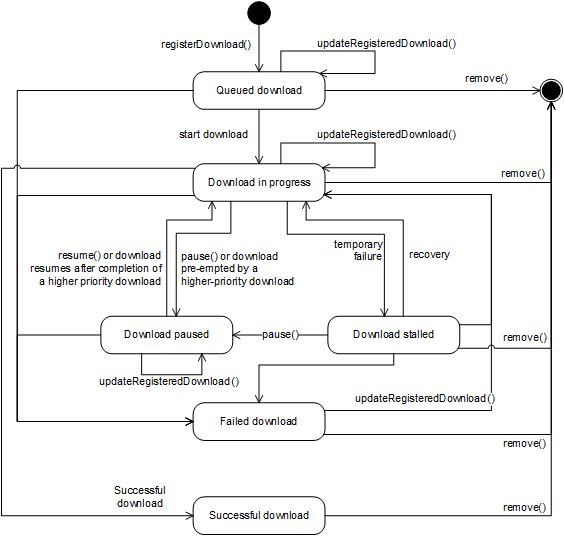
Interface d6: Although the download manager is an autonomous
process, the user may sometimes want to view or control the state of the
download manager. To this end, the download manager will typically
offer its own user interface, which allows the user to manage the
ongoing downloads (e.g. suspend/resume, cancel) and monitor the progress
of the items that are being downloaded.
In retail deployments this is typically a local user interface, for
which no protocol needs to be defined. However, since it may be useful
for the user to have a quick overview of the current downloads, in
section 7.15.1 of
this document a visualization embedded object called
application/oipfStatusView has been defined by which a (third-party)
server provider could include an overview of the status of the download
manager as part of its UI. This is interface d6 in the figure above.
NOTE: for managed deployments JavaScript interfaces may be needed to
have more control over the UI of the download manager. This is covered
by the download manager APIs in section 7.4.3.
Interface e*: Unicast Streaming and playback of downloaded content using A/V Control object
The A/V Control object as defined in section 7.14 may be used to render unicast streaming content triggered by a content-access streaming descriptor (as specified in section 7.14.1.5) and may be used to play back (partially) downloaded content by using the method setSource as specified in section 7.14.7.
Interface e0 can be used to pass for a content access streaming
descriptor to set up a protected stream, by passing through interface e1
the necessary information for the A/V player to set up the stream
through interface e2, and for passing included
<DRMControlInformation> messages to the DRM agent for DRM
protection of the streamed content using interface f.
Interface e0 can also be used to get feedback from the A/V player (such as DRM related playback errors as defined in section 7.13.5) in case of playing streaming content or partially downloaded content (through method setSource()).
Interface f: Request license
The A/V Player will render the content. When the content is
protected, the A/V embedded object will have to get the necessary keys
from the DRM agent using interface f in order to decrypt the content.
If the content is played inside the browser, interface e1 defines a callback event “onDRMRightsError” to allow the page to handle DRM-related errors (in addition to c1).
Interface g*: Local metadata based applications
These interfaces are for use with local OITF embedded and DAE
applications that may wish to use a metadata CG client for browsing and
selecting the content.